

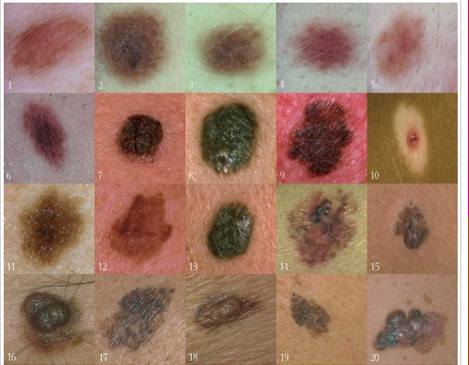
Prevent the damage with the use of a broad spectrum sun-screen at all times whilst in the sun, and do not allow your skin to burn, 3 burns in your lifetime increases you risk of skin-cancer! Slip, slap and slop it on, as the Australians say! A teaspoon of sun-screen for your face and a shot glass for your body and re-apply regularly.įor more information visit the Skin Cancer Foundation. Some melanomas do not conform to the A-B-C-D-E criteria, so any suspicious ones should be examined by a Doctor/Dermatologist. The following ABCDE system can help you tell a normal mole from one that could be melanoma, check your self and your family at least once a year and anything suspicious should be seen by your doctor immediately.Īsymmetry – Melanoma lesions are typically asymmetrical, whereas benign moles are typically round and symmetrical.īorder – Melanoma lesions frequently have uneven or irregular borders (e.g, ragged or notched edges), and benign moles have smooth, even borders.Ĭolour – Melanoma lesions often contain multiple shades of brown or black, whereas benign moles are usually a single shade of brown.ĭiameter – Early melanoma lesions are often more than 6mm in diameter, whereas benign moles are usually less than 6mm in diameter.Įlevations or Enlargement – look out for moles that seem much bigger or more raised. Most people have moles that are almost always harmless, however it is vital to recognise the changes in your moles that may suggest melanoma is developing.
Once a mole develops, it normally stays the same size, colour and shape for many years. Moles can appear on areas of your skin that have had more sun-exposure than others. Moles are normally smaller than a quarter of an inch in diameter and can be present at birth or just appear during your childhood or adulthood. They can be raised or flat, oval or round. An ordinary mole is normally an even colour and can be light brown, tan or a black spot on the skin. It is important to know the difference between an ordinary mole and melanoma, since moles may develop into melanoma or indicate an increased risk for melanoma. It wasn’t dark and didn’t appear larger, it just kept bleeding slightly. The mole on Robs face didn’t look like the ones that you see in photos. How do you know when a mole needs checking out? Rob did need a strict talking to by the dermatologist as for some reason he thought that once the moles were removed he was ok to wear a low factor sunscreen. We were lucky to find a fantastic surgeon who managed to remove them without causing too much scarring. it was a small melanoma, he also had two on his back. ABC Order with Caterpillars Keyboard Consonant and Vowels. ABC Whack a Mole ABC Order with Caterpillars. ABC typing games, ABC puzzles, with your favorite characters like Mickey Mouse. I noticed that a small mole had changed on his face and eventually got him to see a dermatologist. Synthesis: a mole with diameter of 6 millimeter, that it introduces alterations - irregular asymmetry, edges, color - must induce the patient to address early on dermatologist to careful clinical and dermatoscopic examination and consequently, if necessary, to surgical removal of the lesion, with successive hystological examination. ABC learning games for children, from 3 years old to 12 years old. Even in recent years he ignored my pleas for him to use high factor SPF.
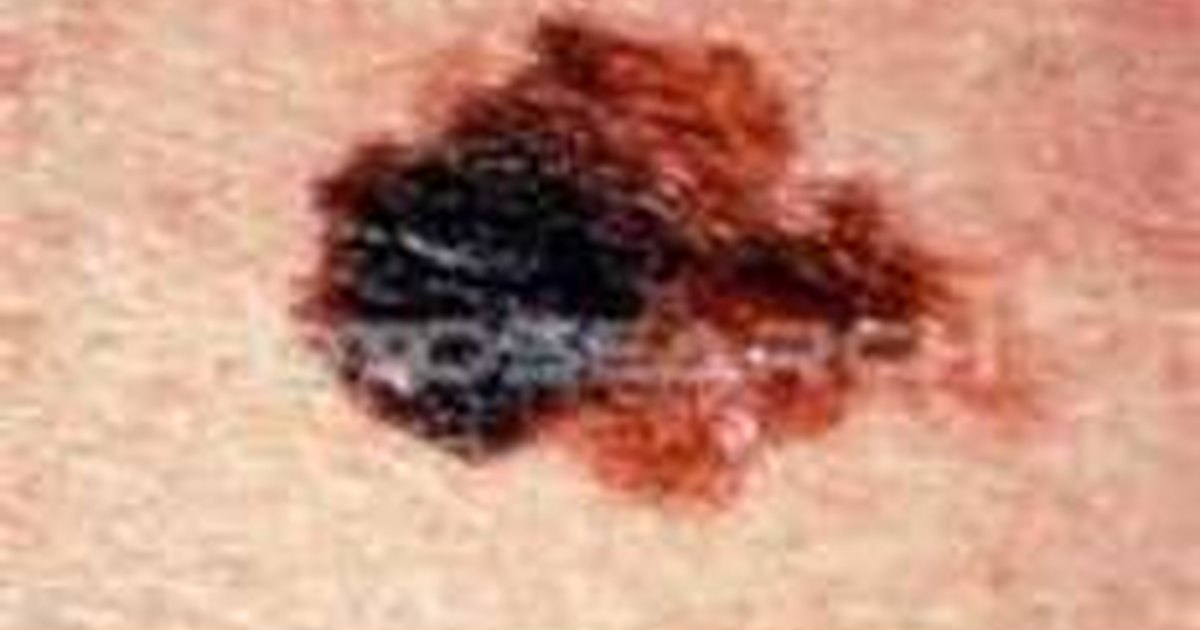
You can imagine that being red haired and no real sun cream would be the worst scenario for his skin. This change may be in size and shape or in symptoms such as itching, bleeding or scabbing. Early melanoma may be flat and any change is a concern. E levation/evolution: as melanoma progresses, it may grow down and up from the skin, becoming elevated. When he left school he signed up as an engineer in the navy he spent much of his time in the Middle East. Increasing size, especially over 6mm diameter is more concerning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
